Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Species | Mouse |
| Antigen | SIRP-α |
| Synonyms | BIT, Brain Ig-like molecule with tyrosine-based activation motifs, CD172 antigen-like family member A, Macrophage fusion receptor, MFR, MYD1, P84, protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type substrate 1, PTPNS1, SHP substrate 1, SHPS1, SHPS1CD172A, Signal-regulatory protein alpha-2, SIRP alpha |
| Accession | P97797-1 |
| Amino Acid Sequence | Lys32-Asn373, with C-terminal 10*His KELKVTQPEKSVSVAAGDSTVLNCTLTSLLPVGPIRWYRGVGPSRLLIYSFAGEYVPRIRNVSDTTKRNNMDFSIRISNVTPADAGIYYCVKFQKGSSEPDTEIQSGGGTEVYVLAKPSPPEVSGPADRGIPDQKVNFTCKSHGFSPRNITLKWFKDGQELHPLETTVNPSGKNVSYNISSTVRVVLNSMDVNSKVICEVAHITLDRSPLRGIANLSNFIRVSPTVKVTQQSPTSMNQVNLTCRAERFYPEDLQLIWLENGNVSRNDTPKNLTKNTDGTYNYTSLFLVNSSAHREDVVFTCQVKHDQQPAITRNHTVLGFAHSSDQGSMQTFPDNNATHNWNGGGSGGGSHHHHHHHHHH |
| Expression System | HEK293 |
| Molecular Weight | 60-90kDa |
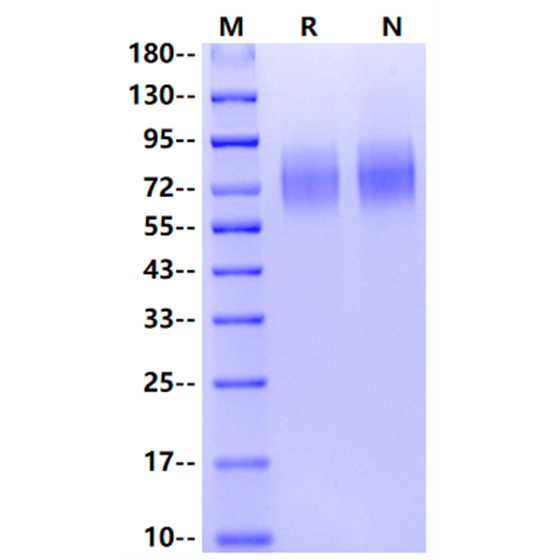
| Purity | >95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1EU/μg |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Tag | His Tag |
| Physical Appearance | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage Buffer | PBS, pH7.4 |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation. |
| Stability & Storage | · 12 months from date of receipt, lyophilized powder stored at -20 to -80℃. · 3 months, -20 to -80℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · 1 week, 2 to 8℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference | 1. Barclay, A.N. & M.H. Brown (2006) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6:457. 2. vanBeek, E.M. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:7781. 3. Liu, Y. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:36132. 4. Kharitonenkov, A. et al. (1997) Nature 386:181. |
Background
Signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRP alpha, designated CD172a), also called SHPS-1 (SHP substrate 1) and previously, MyD-1 (Myeloid/Dendritic-1), is a monomeric ~90 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein that belongs to the SIRP/SHPS (CD172) family of the immunoglobulin superfamily. SIRPs are paired receptors, with similar extracellular domains but differing C-termini and functions. The 503 amino acid (aa) human SIRP alpha contains a 342 aa extracellular domain (ECD), with one V-type, and two C1 type Ig domains, and three potential N glycosylation sites. It has a 110 aa cytoplasmic sequence with ITIM motifs that recruit tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2 when phosphorylated. SIRP alpha is expressed mainly on myeloid cells, including macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic and Langerhans cells. It is also found on neurons, smooth muscle and endothelial cells. SIRP alpha shows adhesion to the ubiquitous CD47/IAP (integrin associated protein), while SIRP gamma binds more weakly and SIRP alpha 1 does not bind at all. Mouse and human SIRP alpha -CD47 binding only cross-reacts for specific polymorphisms and influences engraftment of xenotransplanted stem cells. SIRP alpha engagement generally produces a negative regulatory signal. Low SIRP alpha recognition of CD47, which occurs on aged erythrocytes or platelets or xenogenic cells, promotes clearance of CD47low cells from circulation. SIRP alpha recognition of surfactants SP-A and SP-D in the lung can inhibit alveolar macrophage cytokine production.
Picture
Picture
Bioactivity
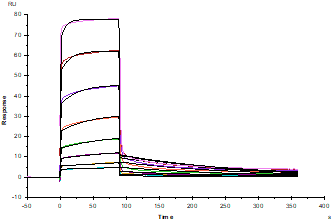
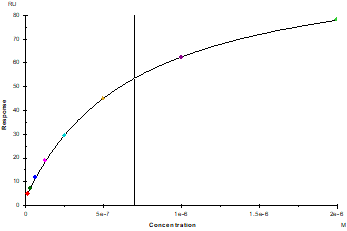
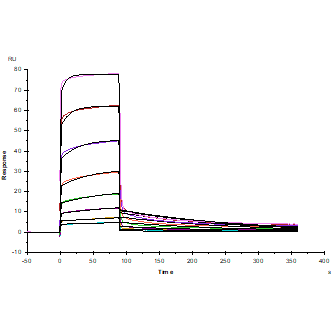
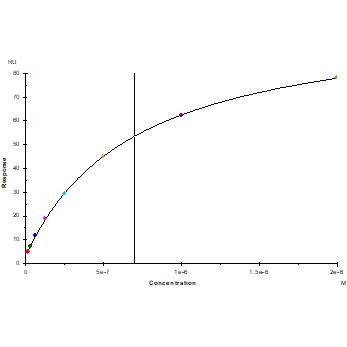
Protein A Chip captured CD47 Fc Chimera, Mouse(Cat. No. UA010266), can bind SIRP-α/CD172A His Tag, Mouse(Cat. No. UA010619) with an affinity constant of 0.70μM as determined in SPR assay.
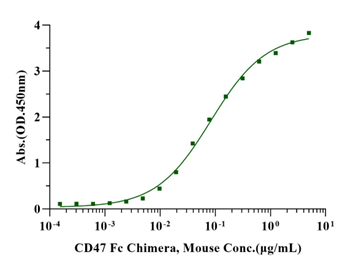
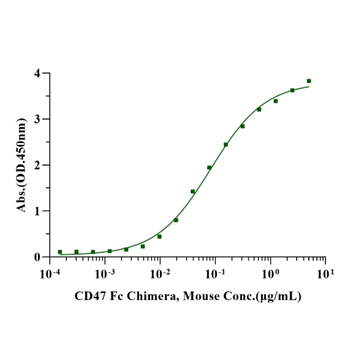
Immobilized SIRP-α/CD172A His Tag,
Mouse (Cat. No. UA010619) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind CD47 Fc Chimera,
Mouse (Cat. No. UA010266) with EC50 of 0.070-0.10μg/ml.
SDS-PAGE
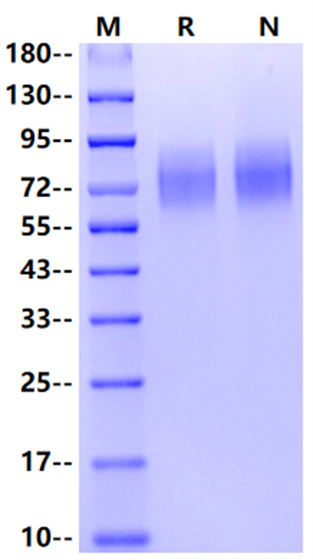
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).