| Description |
Detection Principle:
This kit utilizes double-antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technology. Specific anti-mouse IgG antibodies are pre-coated on a high-affinity ELISA plate. Standards and the sample to be tested are added to the plate wells and incubated. During incubation, IgG present in the sample binds to the solid-phase antibody. After washing to remove unbound material, a detection antibody labeled with horseradish peroxidase is added and incubated. After washing, the chromogenic substrate TMB is added, and color is developed in the dark. The intensity of the color reaction is proportional to the IgG concentration in the sample. The reaction is terminated by adding a stop solution, and the absorbance is measured at a wavelength of 450 nm (reference wavelength 570-630 nm).
Detection Type: Double antibody sandwich assay
Format: Pre-coated 96-well plate
Detection Sample Type: Serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant and other biological samples
Sample Volume: 10 μl
Kit Components: 96-well polystyrene ELISA plate coated with anti-IgG monoclonal antibody, lyophilized mouse IgG standard, IgG detection antibody, standard diluent, horseradish peroxidase-labeled streptavidin, signal enhancer concentrate, signal enhancer diluent, detection buffer (10×), substrate (TMB), stop solution, wash solution (20×), and sealing film.
Sensitivity: 10.70 pg/mL
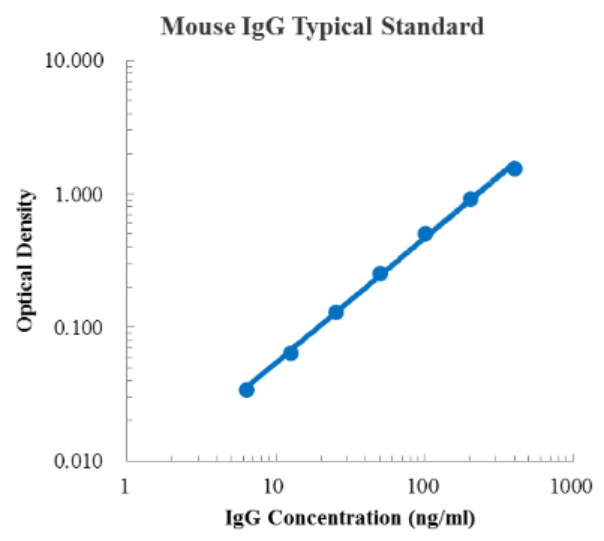
Detection range: 6.25 ng/mL - 400 ng/mL
Recovery range: 89% - 101%
Storage method: 2-8℃
Standard curve:
Background:
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is an antibody, a protein complex composed of four peptide chains—two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains arranged in a Y-shaped antibody monomer. Each IgG has two antigen-binding sites. IgG is the primary antibody found in blood and extracellular fluids, controlling infections in human tissues. Plasma B cells produce and release IgG molecules. IgG is the only immunoglobulin that can cross the human placenta, providing protection to the fetus in utero. IgG antibodies extracted from blood donor plasma can be used as intravenous immunoglobulin to treat immunodeficiency, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases.
|



