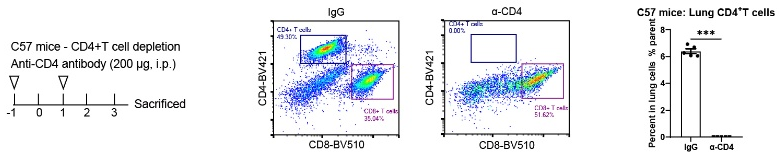
CD4+T cell depletion efficacy of S0B0690 in C57 mice
Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Host | Rat |
| Antigen | CD4 |
| Synonyms | T-cell surface glycoprotein CD4, T-cell differentiation antigen L3T4, T-cell surface antigen T4/Leu-3 |
| Accession | P06332 |
| Clone Number | GK1.5 |
| Antibody Type | Rat mAb |
| Isotype | Rat IgG2b,k |
| Application | in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion |
| Reactivity | Ms |
| Purification | Protein G |
| Concentration | Lot specific* (generally 5 to 10 mg/ml)* |
| Purity | >95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <2EU/mg |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Physical Appearance | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH6.5, containing no preservative |
| Stability & Storage |
2 to 8 °C for 2 weeks under sterile conditions; -20 °C for 3 months under sterile conditions; -80 °C for 24 months under sterile conditions.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background
CD4 is a protein found on the surface of certain immune cells, primarily T helper cells (also known as CD4+ T cells). CD4 stands for "cluster of differentiation 4" and is a glycoprotein that serves as a receptor for major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules, which are present on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells. The primary function of CD4+ T cells is to orchestrate and regulate the immune response. They are crucial in activating other immune cells, including macrophages, cytotoxic T cells (CD8+ T cells), and B cells, to eliminate pathogens and infected cells. CD4+ T cells can be further classified into different subsets based on their function and the cytokines they produce, such as Th1, Th2, Th17, and regulatory T cells (Tregs). CD4 is also used as a marker for identifying and quantifying T helper cells in clinical settings. Decreased CD4 counts are often associated with immune suppression, such as in HIV/AIDS, where the virus specifically targets and destroys CD4+ T cells, leading to a decline in immune function. Monitoring CD4 counts is important in managing HIV/AIDS and assessing the immune status of patients.
Picture
Picture
Validation Data